Background
Methionine adenosyltransferase 2α is a rate-limiting enzyme in the methionine cycle and is also a recognized target for cancer therapy. A number of MAT2A inhibitors have been publicly reported, and three have entered clinical trials for the treatment of solid tumors or lymphomas caused by methylthioadenosine phosphorylase (MTAP) deficiency. Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Agios and many other pharmaceutical companies have developed inhibitors for this target.
Results
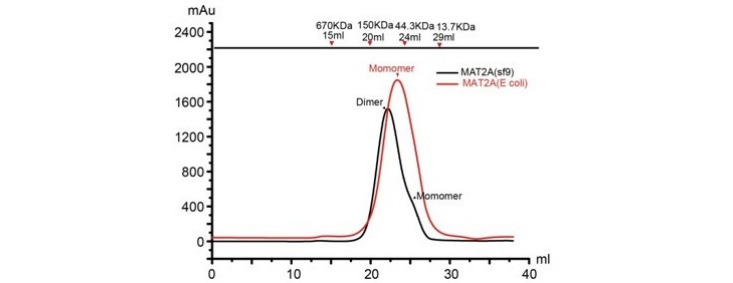
The monomeric MAT2A enzyme cannot perform catalysis because the protein is unable to form a complete active site in the monomeric state. When a dimer is formed, each of the two monomers of the protein contributes half of the residues to form the full active site. To screen inhibitors for MAT2A targets, we need to obtain proteins that are close to the natural environment and form dimers.
We used a conventional prokaryotic protein expression system to express the monomeric MAT2A protein (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1 Results of MAT2A monomer expression and purification
The dimeric MAT2A protein was also successfully obtained by the insect expression system (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2 Results of MAT2A dimer expression and purification
Fig. 3 Gel filtration chromatography results of MAT2A monomer and dimer